Learning objectives
- Learning
- Understand
- Integrate
- Reflect
|
Introduction
- Venous thromboembolism [VTE] is a common, potentially avoidable cause of morbidity and mortality in hospitalised patients
- VTE is common in patients after stroke. Prevention and treatment are key
- Most DVTs develop early, within the first week after the stroke.
| KEY FACTS: Results of the CLOTS-1 and -2 studies showed that graduated compression stockings (either full-length or below-knee) are not effective in preventing VTE in stroke patients. Evidence from the CLOTS-3 study shows that intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC) not only reduces DVT, but also mortality. |
Aetiology: Virchow's triad
- Vessel problems: Stasis and compression of veins
- Blood: Stroke, Infection, Inflammation may be a prothrombotic state
- Flow: obstructed and loss of normal venous pump due to immobility due
Risks
- Old age: risk x 4-6 over age of 70
- Severity of paralysis
- Previously documented DVT
- Dehydration
- Morbid obesity
- Post-partum
- Known thrombophilia
- Malignancy
- Recent Surgery
Epidemiology of Post stroke VTE
- Asymptomatic DVT: up to 50%
- Symptomatic DVT: 3%
- Symptomatic PE: 1%
Clinical
- Pain, swelling of leg may suggest a DVT
- Chest pain and breathlessness, hypotension, cyanosis may suggest a PE
- Stroke/Systemic embolism: Rare paradoxical embolus from VTE can cause stroke
Investigations
- FBC, U&E, ESR, LFTs, CXR, Clotting profile.
- ECG: Sinus tachycardia, RBBB, RAD, S1Q3T3
- Troponin: Elevated Prognostic. Dimer: elevated but not needed if suspicion high
- CT brain before any decision to anticoagulate if not already done
- DVT requires a compression proximal leg vein ultrasound scan
- PE requires a CTPA or a V/Q SPECT scan but if not available, a V/Q planar scan
- If VTE suspected to be part of a malignancy process then CT Chest/abdomen/pelvis and Breast exam/mammogram should be considered
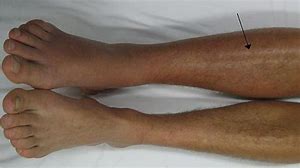
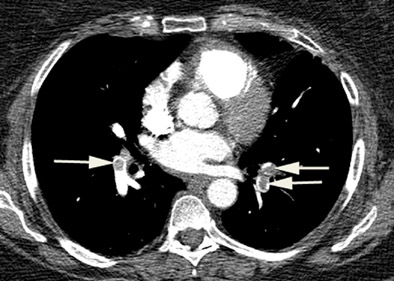
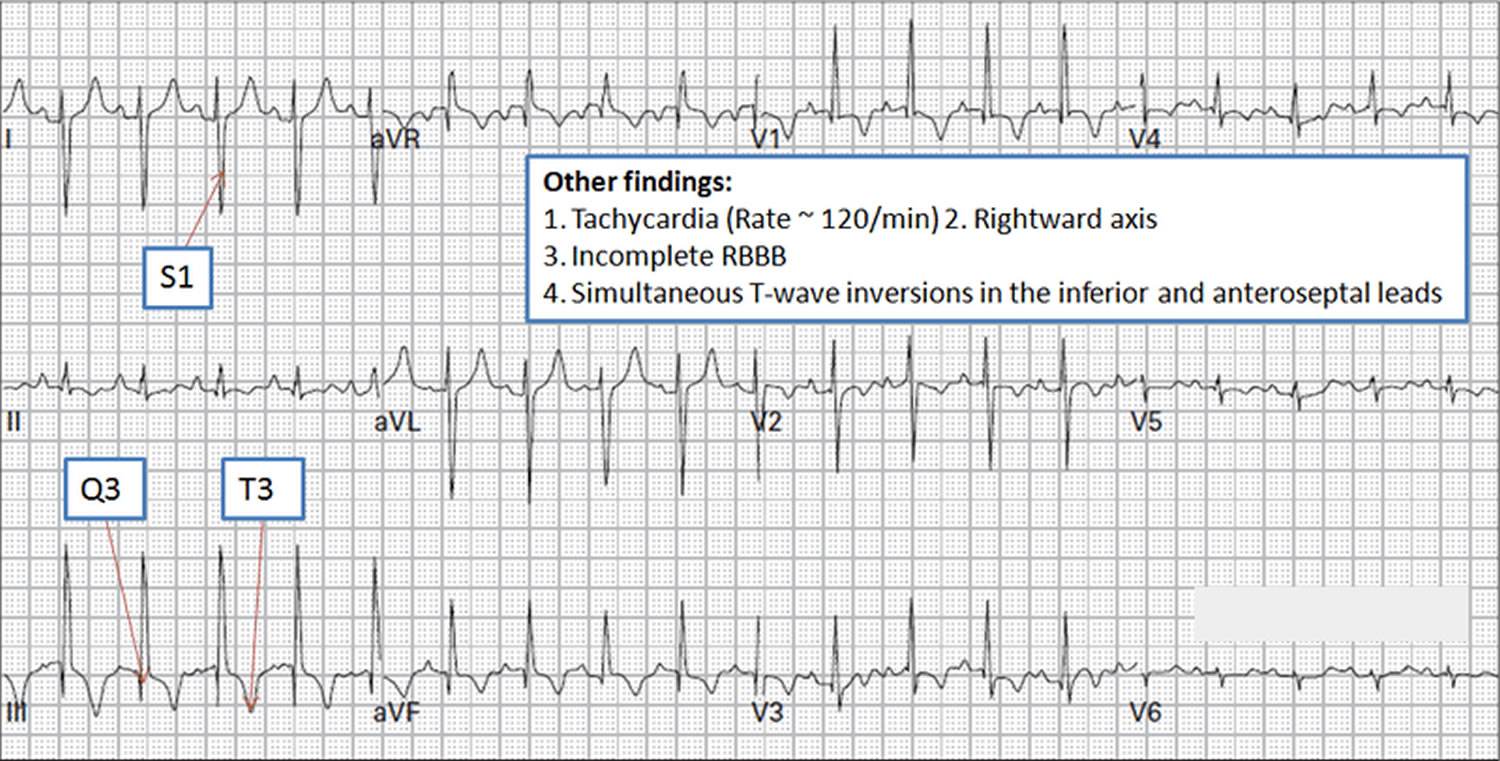
VTE Prevention
- Anticoagulation:Prophylactic anticoagulation with unfractionated or low molecular weight heparin prevents DVTs but increases risk of intracranial and extracranial haemorrhage. The benefits are cancelled out. In fact the trials stated that prophylactic/low-dose heparin increased symptomatic ICH by more than they reduced symptomatic PE in patients with recent ischaemic stroke and cannot be recommended, but they may still be relevant in patients at very high risk of PE (e.g., morbid obesity, previous venous thromboembolism, and inherited thrombophilia) or if started later, although trials have not assessed these issues [1]. Prophylactic anticoagulation is not recommended for unselected stroke patients in the UK stroke guidelines [2].
- Compression stockings:The CLOTS-1 and -2 studies [3] showed that graduated compression stockings (either full-length or below-knee) are not effective in preventing VTE in stroke patients.
- Intermittent pneumatic compression: Evidence from the CLOTS-3 study [4] shows that intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC) reduces DVT and mortality. This should be started within three days of hospitalization and be provided continuously for 30 days, or until the patient is mobile or discharged
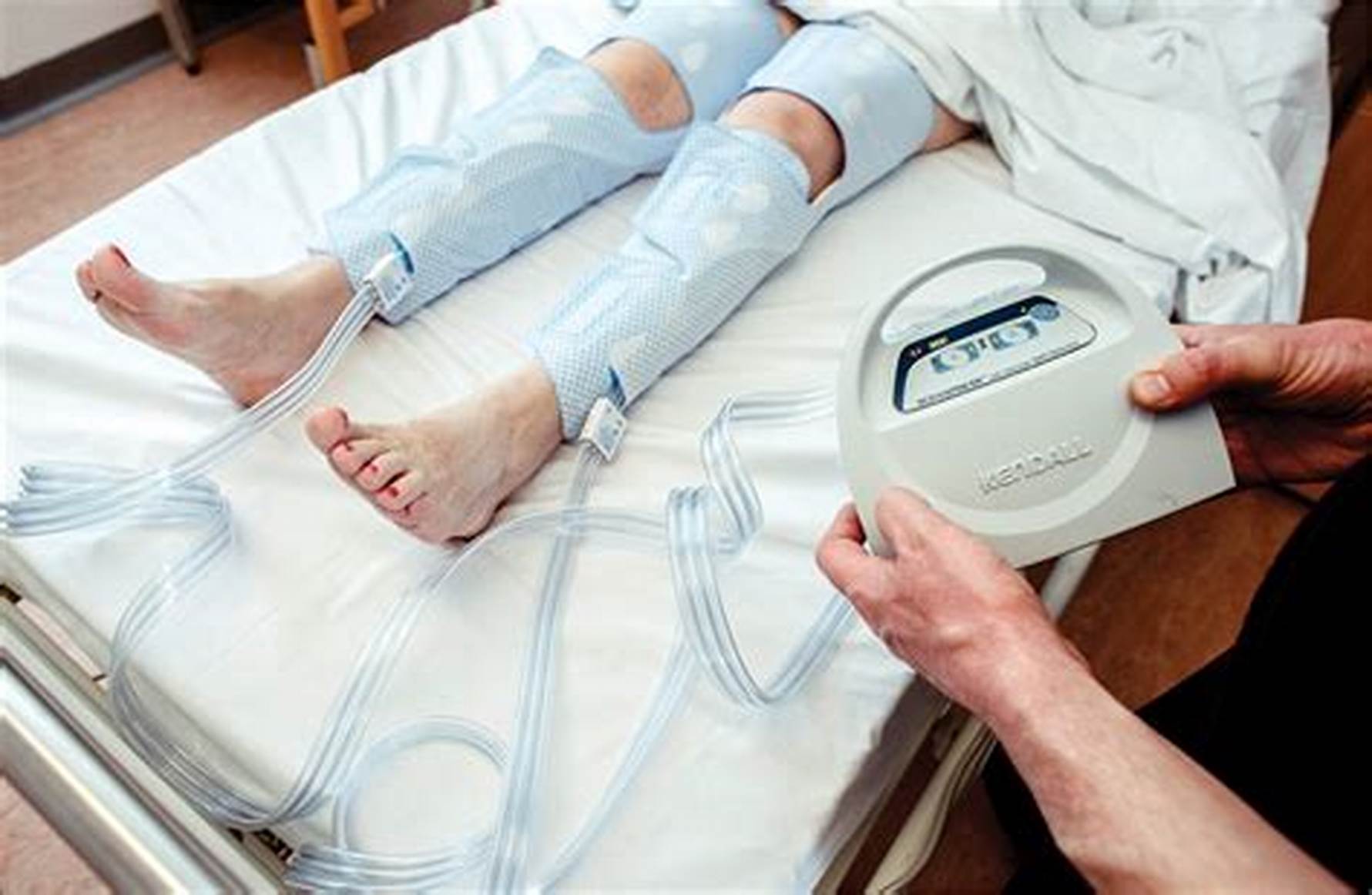
VTE Management
- ABC If haemodynamic instability start IV fluids and ensure volume filled and give oxygen to support patient if SaO2 < 95%. In some cases patients with an Acute PE a patient my be pulseless and not breathing and may need resuscitation depending on resuscitation status. There are a variety of treatments but these are limited as they may have significant haemorrhagic risk. Occasionally one can only support with fluids, oxygen and after a few days patients may improve. Difficult cases likely to benefit from discussions with other experts and family.
- Ischaemic stroke: If a PE or symptomatic proximal DVT is diagnosed or there is a high degree of certainty in patients with ischaemic stroke, full therapeutic anticoagulation is recommended. Warfarin or DOACs may be considered based on licensing and a balance of risks and benefits. They are continued for approximately 12 weeks depending on the ongoing risk profile and then a reassessment is made.
- Haemorrhagic stroke: In those with an intracerebral haemorrhage, a vena cava filter might be an alternative, but this also requires anticoagulation in the longer term. IVC filters have an acceptable safety profile in stroke patients and appear to be effective in preventing life-threatening PE [5]. They do not treat the current PE which must be managed supportively. At a later stage anticoagulation may be started usually beyond 2 weeks but this must be based on an assessment of further VTE and ICH risk.
- Catheter Thrombolysis to treat DVT Consider catheter-directed thrombolytic therapy for patients with symptomatic iliofemoral DVT who have symptoms of less than 14 days' duration and good functional status and a life expectancy of 1 year or more and a low risk of bleeding. This may be feasible in some patients with ischaemic stroke. Discuss with interventional radiology.
- Systemic thrombolysis: Consider systemic thrombolytic therapy in patients with PE and haemodynamic instability but this must be on a case by case assessment as it may result in the real risk of haemorrhagic transformation for those with ischaemic stroke and would be contraindicated in haemorrhagic stroke.
References
- [1] Geeganage, C.M.; Sprigg, N.; Bath, M.W.; Bath, P.M. Balance of symptomatic pulmonary embolism and symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage with low-dose anticoagulation in recent ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 22, 1018-1027.
- [2] Intercollegiate Stroke Working Party. National Clinical Guideline for Stroke, 5th ed.; Royal College of Physicians: London, UK, 2016.
- [3] Collaboration, C.T.; Dennis, M.; Sandercock, P.; Reid, J.; Graham, C.; Murray, G.; Venables, G.; Rudd, A.;
Bowler, G. The effect of graduated compression stockings on long-term outcomes after stroke: The CLOTS trials 1 and 2. Stroke 2013, 44, 1075-1079.
- [4] Dennis, M.; Sandercock, P.; Graham, C.; Forbes, J.; Collaboration, C.T.; Smith, J. The clots in legs or stockings after stroke (CLOTS) 3 trial: A randomised controlled trial to determine whether or not intermittent pneumatic compression reduces the risk of post-stroke deep vein thrombosis and to estimate its cost-effectiveness. Health Technol. Assess. 2015, 19, 1-90.
- [5] Somarouthu, B.; Yeddula, K.;Wicky, S.; Hirsch, J.A.; Kalva, S.P. Long-term safety and effectiveness of inferior vena cava filters in patients with stroke. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2011, 3, 141-146.



