Learning objectives
|
The brain is contained within a bony box but there are also rigid structures within the skull which help to maintain the position of the brain and prevent excessive brain movements in response to rapid acceleration or deceleration forces. The falx lies in the midline and separates the lobes but also helps prevent excessive movement. The tentorium or "tent" separates the forebrain from the brainstem. Excessive forces within the skull can distort and squeeze neural structures which can be a sign of impending death. Seen in the context of rising ICP in the comatose patient. These are all neurosurgical emergencies and demand rapid escalation. There are three main forms
Herniation syndromes
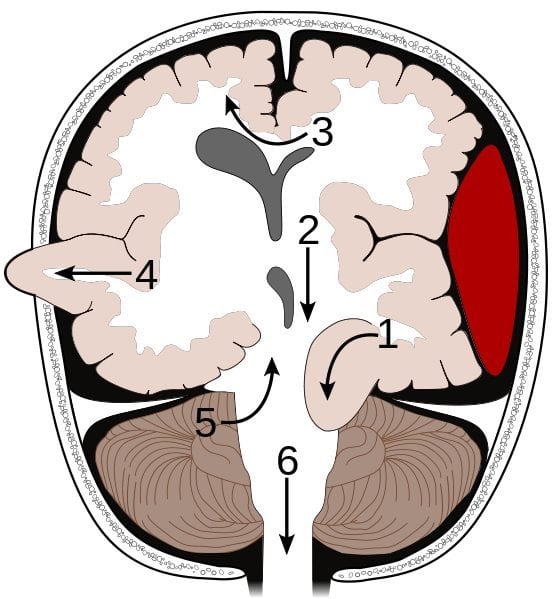
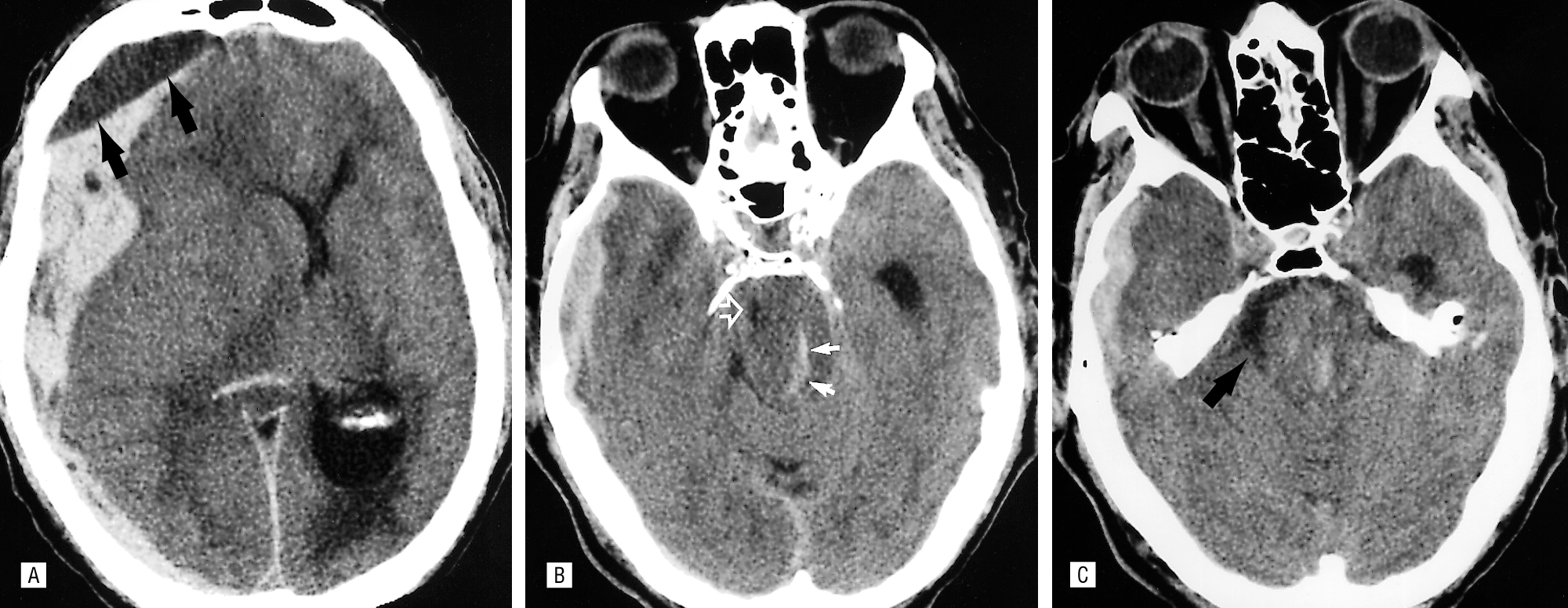
No. Syndrome Segment affected Details [1] Transtentorial Medial temporal lobe (uncus), IIIrd nerve, PCA Here an asymmetrical supratentorial mass or pressure gradient forces the uncus of the temporal lobe down beneath the tentorium 'tent' can result in an ipsilateral oculomotor paresis (dilated pupil, ptosis, down and out pupil) and compression of the posterior cerebral artery giving contralateral hemianopia. The shift forces the opposing cerebral peduncle against the edge of the tentorium causing contralateral hemiparesis to the peduncle. The indentation of the tentorium edge causes Kernohan's notch on the opposite cerebral peduncle. This is a false localising sign. Extensive brainstem ischemia may occur due to bleeding in the midbrain and upper pons with formation of Duret haemorrhages. [2] Central transtentorial hernation Thalamus There is a symmetrical downward movement of the thalamic region through the opening of the tentorium cerebelli with progressive coma [3] Subfalcine Cingulate gyrus Here the brain is pushed down and laterally under the falx separating right and left cortices. It is often due to a lobar mass or oedema or an extra-axial mass such as a subdural or extradural bleed. There may be compression of the anterior cerebral artery and stroke involving the as it is nipped by the edge of the falx with contralateral leg weakness. The lateral ventricles and brain midline will be distorted and shifted and can be seen on CT. Clinical effects in themselves mild but depend on the underlying cause [4] Transcavarial Cortex Seen after there has been a hemicraniectomy or there has been a fracture or some other skull lesion and the brain herniates outside the margins of the skull until the oedema settles. [5] Upward transtentorial herniation (“reverse coning”) Cerebellum So-called “reverse coning” can occur if an EVD is inserted for hydrocephalus due to a posterior fossa mass lesion. This leads to upwards transtentorial herniation of posterior fossa contents. [6] Transforaminal (Tonsillar "Coning") Cerebellar tonsils and medulla There is a huge ICP pressure that is forcing the brain down and out of the skull through the foramen magnum. Result is that the brainstem and cerebellar tonsils are forced down into the foramen magnum and pressure on the medulla leads to apnoea and death. Uncal herniation due to a SDH with Duret haemorrhages
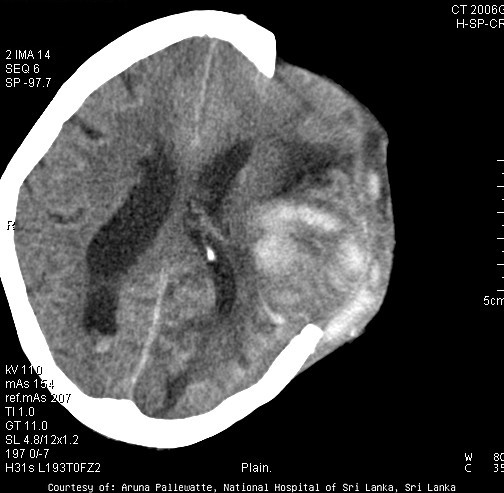
Trancavarial herniation
Clinical signs of Raised ICP
Investigations
Management