Learning objectives
- Relevant as a stroke mimic
- What is ADEM syndrome
- Recognition of ADEM syndrome
- Treatment of ADEM syndrome
|
Introduction
- Relevant as a stroke mimic and so should be identifiable
- Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis mainly affects children but can affect adults
- Inflammatory condition of brain and spinal cord that damages myelin
- May follow a viral illness or have another precipitant
| Many patients initially diagnosed with ADEM develop clinically definite MS upon long-term follow-up. |
Aetiology
- Classically acute and monophasic but not always
- Usually affects young adults and children
- Pathological hallmark of ADEM is perivenular inflammation with limited "sleeves of demyelination"
- CSF elevated IFN-gamma, IL-6, and IL-8
Precipitants
- Bacterial infections: mycoplasma, Gram negative organisms, salmonella typhi
- Vaccination for measles, mumps, or rubella.
- Post viral:Measles, varicella, rubella, Herpes-zoster, Infectious mononucleosis
- Cerebral malaria
Clinical
- Fever, meningism, seizures, coma, usually monophasic but not always
- Weakness, hemianopia, neglect
Investigations
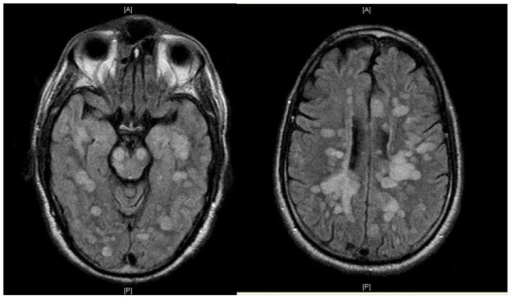
- CT: may show cerebral oedema
- MRI scan:large symmetrical lesions with basal ganglia and thalamus involved.
- LP: raised protein and slight increase in WCC in 80%.Protein > 100mg/dl. No oligoclonal bands
- Brain biopsy: consistent with demyelination.
Differentials
- Multiple sclerosis
- Susac syndrome
- Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
Management
- Mortality is up to 30%
- Treat with high dose IV Methylprednisolone
- Alternatives include Plasmapharesis, IVIG and Rituximab
References and further reading
|
|
Note: The plan is to keep the website free through donations and advertisers that do not present any conflicts of interest. I am keen to advertise courses and conferences. If you have found the site useful or have any constructive comments please write to me at drokane (at) gmail.com. I keep a list of patrons to whom I am indebted who have contributed. If you would like to advertise a course or conference then please contact me directly for costs and to discuss a sponsored link from this site.
|